How do we find the sum of the numbers 1 through 100?
For example,
In code this would look like:
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}If you sum up these numbers, the result is .
Sum of n integers equation
Instead of adding up the numbers 1 through by hand or in a loop, we can use an equation to find the answer instantly.
This is the equation for the sum of integers 1 through :
We can use this equation to find the sum of numbers 1 through 100:
Doing the calculation:
Proof
Visual proof
One way to understand this is to imagine stacking boxes like stairs. You have one box, then two boxes stacked, then three, and so on.
The bottom and side are both length . We need to find the “area” to get the total sum.
We can create a rectangle by duplicating this stack and flipping it upside down:
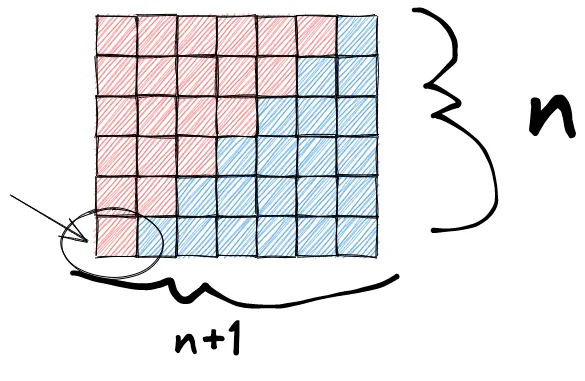
Notice that by flipping it, one side is and the other is .
The area of a rectangle is length times width, which gives us .
We divide by two because we only want the original staircase (half the rectangle).
This gives us the final equation:
Proof by induction
Base case
The base case is the sum of just the first number, so let :
This checks out.
Inductive step
Now let’s find the next sum in terms of :
To find the next sum, we take the sum so far and add the next number to it:
We replace the summation with the original equation and simplify:
To add these terms, we need a common denominator. We replace with the equivalent :
Factor out from both terms:
We can rewrite this to match the original equation’s form:
This looks like the original equation with substituted for :
- Original:
- With :
This completes the induction. We’ve shown the base case holds, and that if the formula works for , it also works for . Therefore the formula works for all positive integers.